To improve fundamental knowledge on material aging, state of the art experimental facilities are necessary. Have a look on some experimental works performed in MAI members’ facilities.

Chemical analysis laboratory (EDF)
Issues
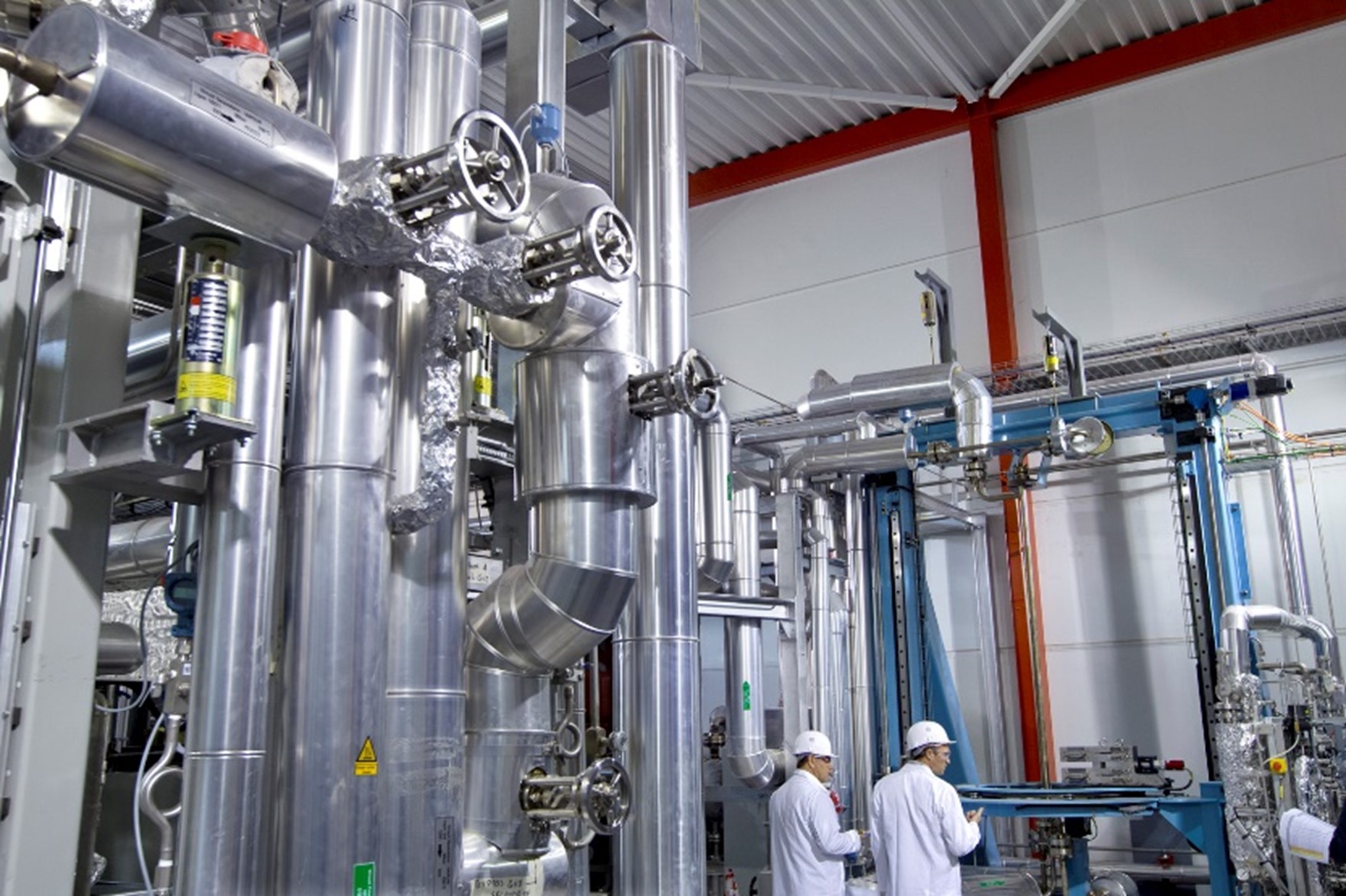
The Chemical analysis laboratory is dedicated to performing chemical analyses in support of R&D studies, particularly those on corrosion of metallic materials, fouling and clogging of steam generators, and chemistry of aqueous solutions, mainly in the nuclear field. The laboratory also carries out special tests such as on ion exchange resins, nuclear waste storage, sorption with zeta potential measurements.
 Our activities
Our activities
– Operation of test loops (FORTRAND, ECCLIPS and SOLO) with the aim of simulating problems encountered on site.
– Chemical analysis services related to R&D studies (boron/lithium matrix, secondary amines, metals, anionic and cationic impurities up to ultra-trace).
– Analysis services for external clients.

Laboratory Non Destructive Testing NDT (EDF)
 Issues
Issues
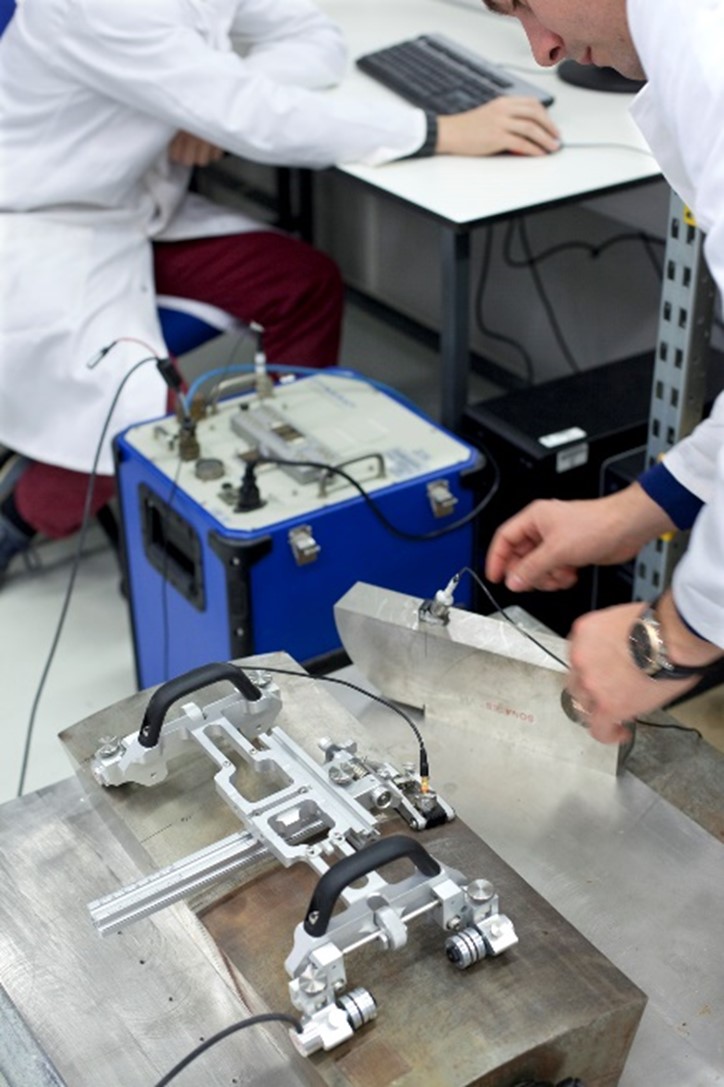
– Understanding the physical phenomena of an ultrasonic inspection
– Support for the qualification of ultrasonic testing processes
– Experimental validation of simulation codes
Studies
– Impact of metallurgical structure on control performance
– Experimental analysis and simulation of the controllability of materials with complex structures (heterogeneous and anisotropic welds, cast steels)
– Development of innovative control techniques

GC Laboratory (Civil Engineering, EDF)
Issues 
– Optimize the maintenance strategy of nuclear power plant enclosures and air coolers.
– Ensure responsible management of radioactive waste.
Studies
GC lab tests improve the understanding of the evolution and aging of civil engineering materials. The results contribute to the development of multi-scale models and behavioural laws used in numerical simulations to support the issues at stake.
Description of the test facility
The Civil Engineering Laboratory is composed of 10 test rooms ranging from the manufacture and preparation of specimens to creep tests, mechanical resistance, determination of the hydrous properties of materials by drying, calorimetry, determination of water porosity on specimens. Its mission is to characterize experimentally the mechanical, chemical and diffusion properties of concretes, their constituents and geo-materials (argillite) in order to feed the studies. Concrete virtual laboratory: To complete the experimental test means, the research engineers develop the Vi(CA)2T software, a real digital laboratory, which allows to obtain physical characteristics of concrete not experimentally accessible (technically unfeasible test, specimens not available, tests of new concrete formulations)

Electron Microscopy Laboratory (EDF)
 Issues
Issues
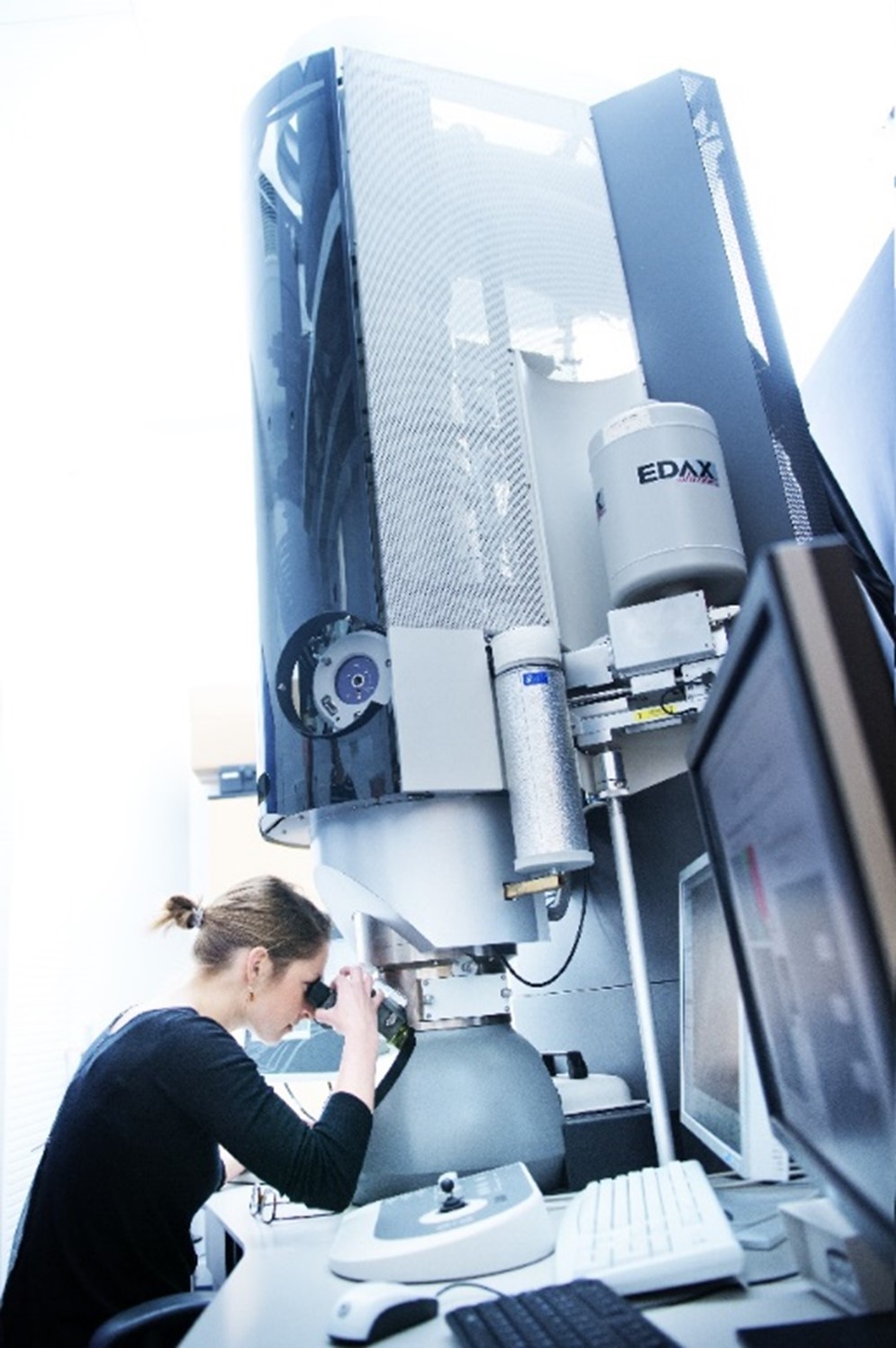
Characterization and analysis of materials at small scales: chemical, physical and microstructural analyses.
Upstream research and expertise carried out for the production and engineering facilities in order to understand the physico-chemical and micromechanical mechanisms related to the ageing of materials in operation.
Description of the test means :
– Transmission electron microscopes: TITAN and Osiris
They allow fine analysis of component materials down to the atomic scale. Their possibilities range from chemical analysis to diffraction (microstructure) through high-resolution imaging and spectroscopy (with an energy resolution close to what is accessible at the synchrotron).
– Scanning Electron Microscopes: Dual Beam, Quanta Environmental SEM and MIRA Micromechanical SEM
Complementary microscopes allowing a large number of analyses to be carried out: types of oxides formed on the surface, mechanical behaviour on the micrometer scale, observation of concrete, 3D imaging, in situ tests in a controlled atmosphere and temperature, or preparation of samples for the TEM in a very localised manner (e.g. crack bottom).

Polymers and Composites Laboratory (EDF)
 Issues
Issues
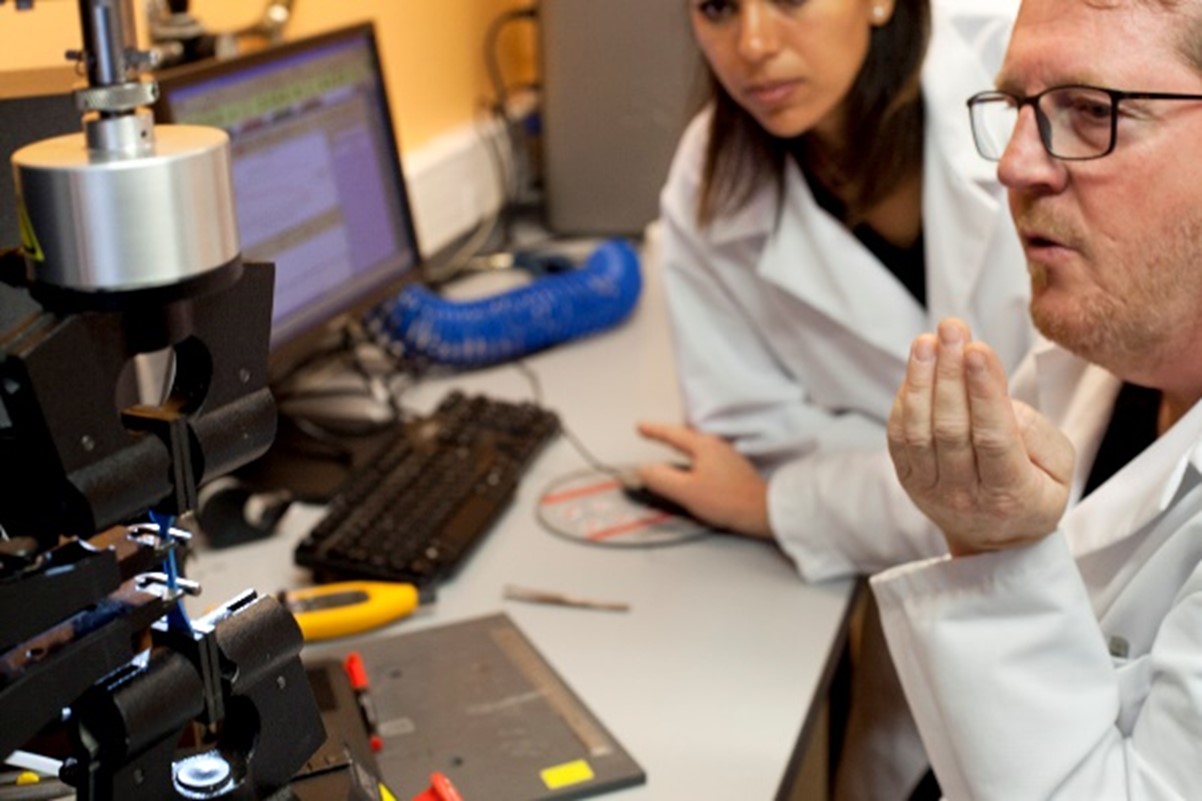
– Experimental expertise in polymer ageing
– Development of NDT techniques for in-service ageing monitoring
– Life-time modeling
– Main subjects of studies: cables, piping, paints, composite coatings,…
Test means for specimen preparation tests
– Milling machine
– Cryogenic microtome
– Trimming machine
– Chainsaw
Accelerated aging test facilities
– Ventilated ovens
– Vacuum ovens/neutral atmosphere
– Humidity (RH) controlled chambers
– Thermostatically controlled tanks in water with neutral, basic, acid pH
Means of physico-chemical and mechanical analysis
– Thermal analysis (TGA)
– Physico-chemical analyses (DSC, Karl Fischer, swelling)
– Chemical analysis (IR, GC-MS, plasticizer quantification)
– Mechanical testing (tensile tests, DMA, hardness)

Mechanical (EDF)
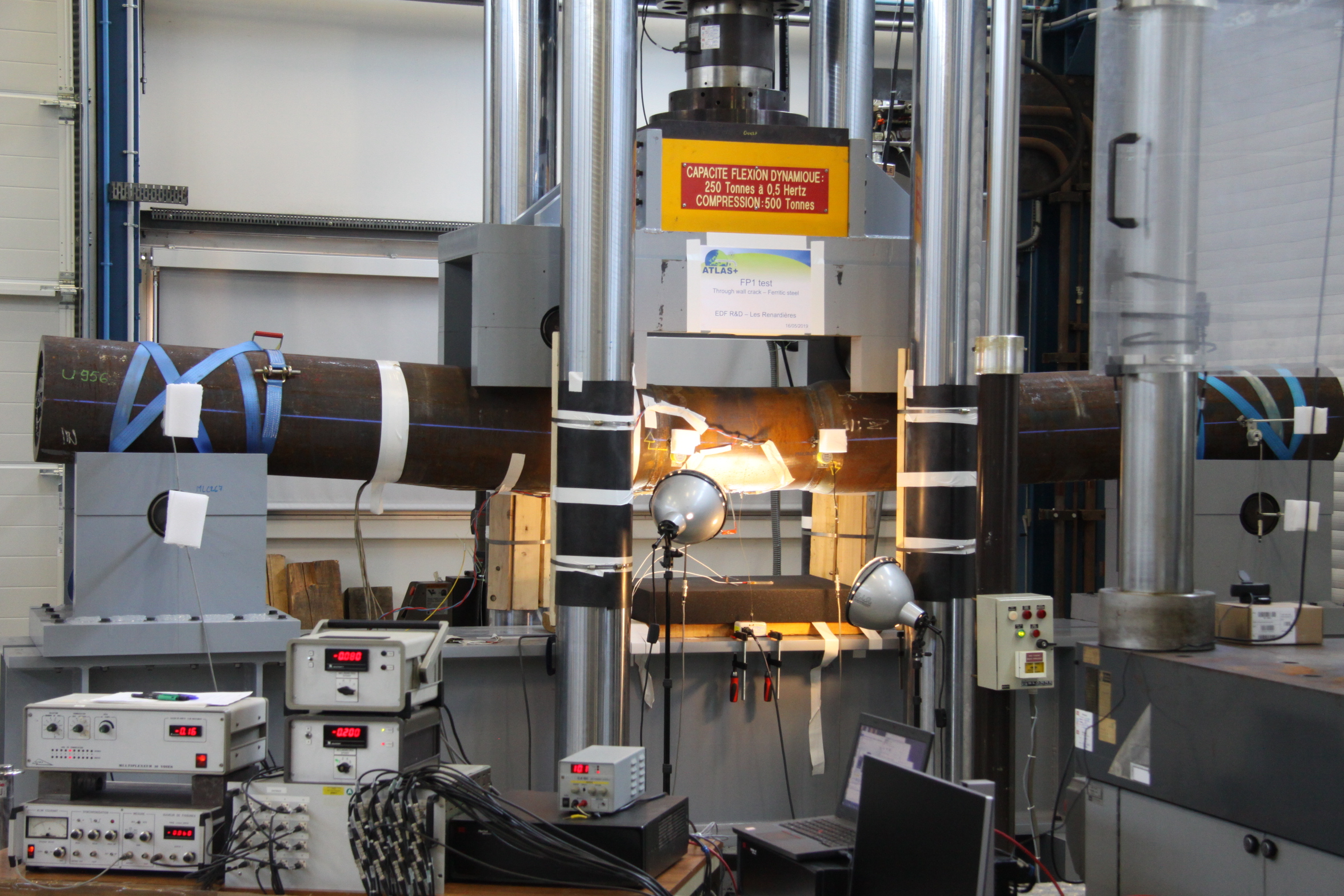 The Mechanical Laboratories provide experimental tools and analysis to study component and material integrity, mechanical degradation, fatigue and creep.
The Mechanical Laboratories provide experimental tools and analysis to study component and material integrity, mechanical degradation, fatigue and creep.
Specific constitutive laws of materials are established to feed numerical models to simulate micro-mechanical behaviour at the crystaline scale.
The laboratory contributes significantly to component lifetime assessments.

Energie (EDF)
 Energy loop is the study of Steam Generator tubes fouling phenomenon. Challenges are : performance : understand fouling mecanisms to save SG thermal performances and predict their evolutions; Availability/safety : optimize maintenance operations (sludge lancing, chemical cleanings, SG replacement,..)
Energy loop is the study of Steam Generator tubes fouling phenomenon. Challenges are : performance : understand fouling mecanisms to save SG thermal performances and predict their evolutions; Availability/safety : optimize maintenance operations (sludge lancing, chemical cleanings, SG replacement,..)
Main objectives are :
- Industrial: identify ways to reduce fouling in order to optimize operation and management of the secondary circuit.
- Modeling: determine inlet date to improve and validate fouling prediction models.

Corrosion Mechanics Environmental Fatigue (EDF)
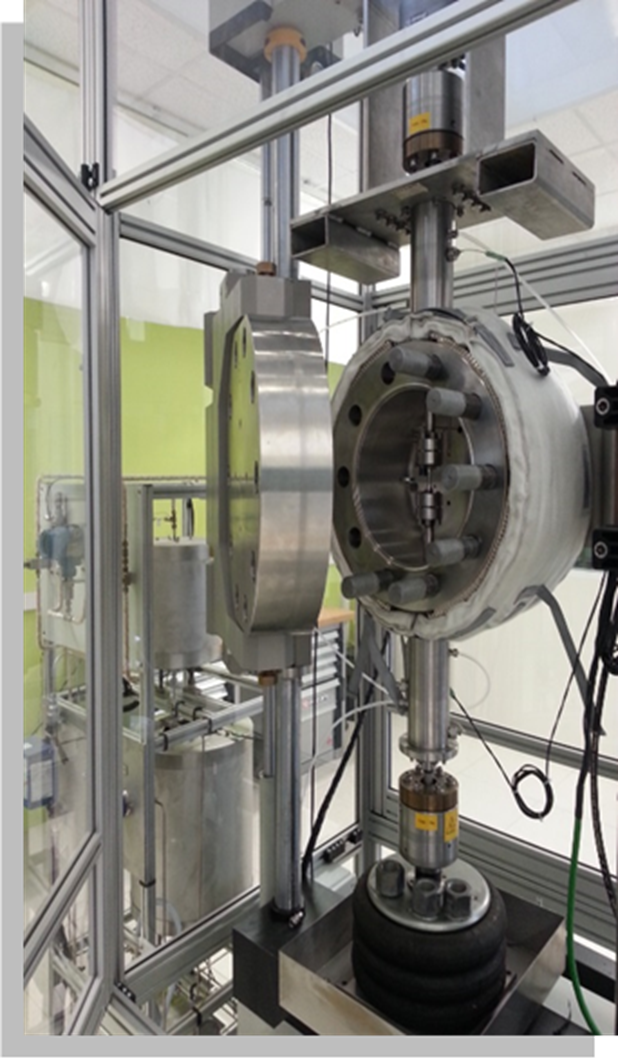 Understanding of stress corrosion degradation phenomena affecting power plant components in primary or secondary environments
Understanding of stress corrosion degradation phenomena affecting power plant components in primary or secondary environments
Description of the test means
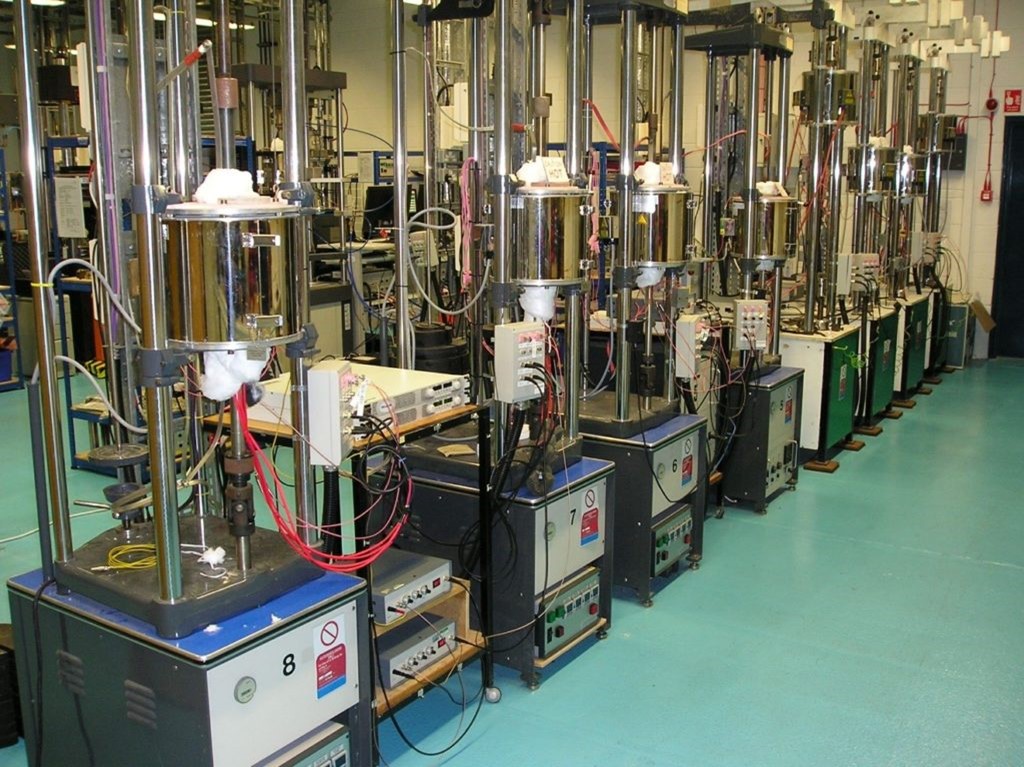
The Corrosion Mechanics Laboratory has 8 test loops and 33 static autoclaves.
7 test loops are dedicated to stress corrosion, 3 are located in the Corrosion Hall (CAMELIA, ACACIA, COSMOS).
One test loop is dedicated to fatigue-corrosion (FATCOR2). The FATCOR2 loop (for FATigue-CORrosion) consists of three modules operating independently for the study of the fatigue properties of materials in the primary environment of nuclear reactors.
Fatigue issues
Assistance in fatigue material coding and understanding of fatigue/corrosion coupling mechanisms










 Discover the Handbook of material ageing management for nuclear reactors
Discover the Handbook of material ageing management for nuclear reactors